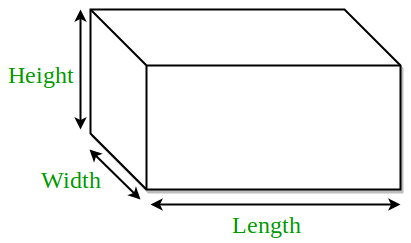
Length, width, height are the three fundamental dimensions used to describe the size and shape of objects in the physical world. These measurements are essential for understanding and communicating the proportions of various items, from small packages to towering skyscrapers.
- Length refers to how long an object is, typically measured from end to end.
- Width (or breadth) describes how wide something is, measured across its shortest side.
- Height indicates how tall or deep an object is, measured vertically.
Together, these dimensions help us visualize and define the three-dimensional space occupied by an object. Whether you’re designing furniture, building a house, or simply measuring a box, understanding length, width, and height is crucial for accurate planning and communication.
What is the Difference Between Length Width Height?
The length, width, height of an object are the different dimensions expressed in linear units. While length is the longest side of a shape, width is the shorter side, and height is the vertical dimension or depth of the shape.
| Dimension | Direction | Common Use |
| Length | Horizontal (longest) | Indicates overall size or distance. |
| Width | Horizontal (shorter) | Shows how wide an object is. |
| Height | Vertical | Represents how tall or deep something is. |
What does LxWxH mean?
However, the industry standard order of dimensions when recording or reading measurements remains the same: Length x Width x Depth (LxWxD) or Length x Width x Height (LxWxH).
LxWxH stands for Length x Width x Height, which is a standard way to represent the three dimensions of an object. It’s commonly used in various fields like geometry, packaging, shipping, and design to calculate the size or volume of an item. Here’s what each term means:
Length (L):
- The longest side of the object.
- Measured horizontally from one end to the other.
- Example: The length of a table or a box’s longest edge.
Width (W):
- The shorter side when measured horizontally, perpendicular to the length.
- Example: The distance across a table from left to right.
Height (H):
- The vertical side, indicating how tall or deep the object is.
- Example: The height of a box measured from its base to the top.
Uses of LxWxH
- Volume Calculation: Multiplying length × width × height gives the volume of a three-dimensional object. For example, the volume of a box is calculated as:
Volume = L × W × H (e.g., 10 cm × 5 cm × 2 cm = 100 cm³). - Shipping and Storage: Knowing LxWxH helps determine how much space an item will occupy.
- Product Dimensions: Manufacturers often specify LxWxH to help customers visualize the product’s size.
Example:
If a package has dimensions 20 cm x 10 cm x 5 cm, it means:
- Length = 20 cm
- Width = 10 cm
- Height = 5 cm
This notation helps ensure clear and uniform communication about the size of the object.
How to calculate height?


Height refers to the vertical measurement of an object from its base to its top. The method for calculating height depends on the context or shape of the object. Here’s a breakdown:
For Simple Shapes (Rectangular or Cuboid Objects):
If you know the volume (V), length (L), and width (W):
- Use the formula:
Height = Volume ÷ (Length × Width)
Example:
A box has a volume of 240 cm³, length of 12 cm, and width of 5 cm.
Height = 240 ÷ (12 × 5) = 240 ÷ 60 = 4 cm
For Triangular Shapes (Area of Triangle):
If you know the base (b) and area (A) of the triangle:
- Use the formula:
Height = (2 × Area) ÷ Base
Example:
A triangle has an area of 30 cm² and a base of 10 cm.
Height = (2 × 30) ÷ 10 = 60 ÷ 10 = 6 cm
For Cylinders (Volume of a Cylinder):
If you know the volume (V) and radius (r) of the base:
- Use the formula:
Height = Volume ÷ (π × Radius²)
Example:
A cylinder has a volume of 314 cm³ and a base radius of 5 cm.
Height = 314 ÷ (3.14 × 5²) = 314 ÷ 78.5 = 4 cm
Using Trigonometry (Inclined Shapes or Angles):
If you have a right triangle and know:
- The hypotenuse (c) and the base (b): Use the Pythagorean theorem:
Height = √(Hypotenuse² – Base²)
Example:
In a right triangle with a hypotenuse of 13 cm and a base of 12 cm:
Height = √(13² – 12²) = √(169 – 144) = √25 = 5 cm
Using Shadows (Objects like Trees or Buildings):
If you know the object’s shadow length and a similar triangle’s dimensions:
- Use the proportionality rule:
Object Height ÷ Object Shadow Length = Known Height ÷ Known Shadow Length
Example:
A tree’s shadow is 10 m, and a 2 m pole’s shadow is 1 m.
Tree Height = (2 ÷ 1) × 10 = 20 m
Measuring Directly (Using Tools):
- Use a measuring tape for straightforward cases like walls or furniture.
- Use devices like an altimeter or laser rangefinder for taller structures.
By understanding the context and available data, you can apply the appropriate method to calculate height effectively.
How to measure width?

Width refers to the horizontal distance across an object or space, typically measured at its broadest part. The method of measuring width varies depending on the object and tools available. Below are different approaches:
Using a Measuring Tape
- Step 1: Place one end of the tape at the starting edge of the object.
- Step 2: Extend the tape to the opposite edge, keeping it level and straight.
- Step 3: Note the measurement in your preferred unit (inches, centimeters, etc.).
Example:
Measuring the width of a table: Start at one edge and measure to the other.
For Rectangular Objects (Mathematical Approach)
If you know the area (A) and length (L) of the object:
- Use the formula:
Width = Area ÷ Length
Example:
A rectangle has an area of 50 cm² and a length of 10 cm.
Width = 50 ÷ 10 = 5 cm
For Cylindrical Objects
The width of a cylinder is its diameter. If you know the radius (r):
- Use the formula:
Width = Diameter = 2 × Radius
Example:
A cylinder has a radius of 7 cm.
Width = 2 × 7 = 14 cm
Using Calipers (For Small Objects)
- Open the caliper and place the object between its jaws.
- Close the jaws until they lightly touch the object’s sides.
- Read the width measurement from the scale or digital display.
Example:
Measuring the width of a coin or small gadget.
For Irregular Shapes
- Step 1: Identify the broadest part of the object.
- Step 2: Use a ruler or tape to measure across this part.
- For highly irregular shapes, use graph paper or a digital scanner to approximate width.
Measuring Width in a Room
- Step 1: Start at one wall and stretch a tape measure to the opposite wall.
- Step 2: Ensure the tape is parallel to the floor and straight.
- Step 3: Record the width in meters or feet.
Tools for Measuring Width
- Measuring Tape: For general use.
- Calipers: For small or precise measurements.
- Laser Distance Meter: For wide or hard-to-reach spaces.
- Ruler: For flat and small objects.
How to measure length?

Length refers to the measurement of the longest side of an object, space, or distance between two points. The method of measuring depends on the object and tools available. Below are detailed steps for measuring length in various scenarios:
Using a Measuring Tape
- Step 1: Place one end of the measuring tape at the starting point of the object.
- Step 2: Stretch the tape along the length of the object to its opposite end.
- Step 3: Read the measurement at the endpoint, ensuring the tape is straight and level.
Example:
Measuring the length of a table or a piece of fabric.
Using a Ruler
- Step 1: Align the ruler’s edge with the starting point of the object.
- Step 2: Mark the endpoint if the ruler is shorter than the object, then move the ruler and continue measuring.
- Step 3: Add up the segments to determine the total length.
Example:
Measuring the length of a pencil or book.
Using a Laser Distance Meter (For Large Spaces)
- Step 1: Position the laser meter at one end of the object or space.
- Step 2: Point the laser to the other end.
- Step 3: The device will calculate the distance and display the length digitally.
Example:
Measuring the length of a room or hallway.
Measuring Irregular Shapes
- Use a flexible measuring tape or string to follow the contour of the object.
- Straighten the string and measure its length using a ruler or tape measure.
Example:
Measuring the length of a curved pipe or irregular object.
For Digital or Scaled Objects
- Open the object in a design or image editing tool like Photoshop.
- Use the ruler or dimension tools in the software to measure length.
Example:
Measuring the length of a rectangle in a digital drawing.
Tools for Measuring Length
- Measuring Tape: Most versatile for various objects.
- Ruler: Ideal for smaller objects.
- Laser Meter: Accurate for large spaces.
- Measuring Wheel: Great for outdoor distances.
- String or Flexible Tape: Best for curved or irregular shapes.
Conclusion
Understanding and measuring length, width, and height are fundamental skills used in everyday life, from home improvement projects to scientific applications. Each dimension serves a unique purpose:
- Length measures the longest side or distance.
- Width refers to the side perpendicular to the length, often representing breadth.
- Height measures the vertical distance or how tall something stands.
By using the right tools like measuring tapes, rulers, laser meters, or specific formulas, you can obtain accurate measurements tailored to your needs. Whether calculating the dimensions of a room, determining the size of an object, or working with digital designs, mastering these measurements ensures precision and efficiency.
Proper understanding of these terms also makes interpreting and communicating dimensions much easier, ensuring success in various tasks and projects.